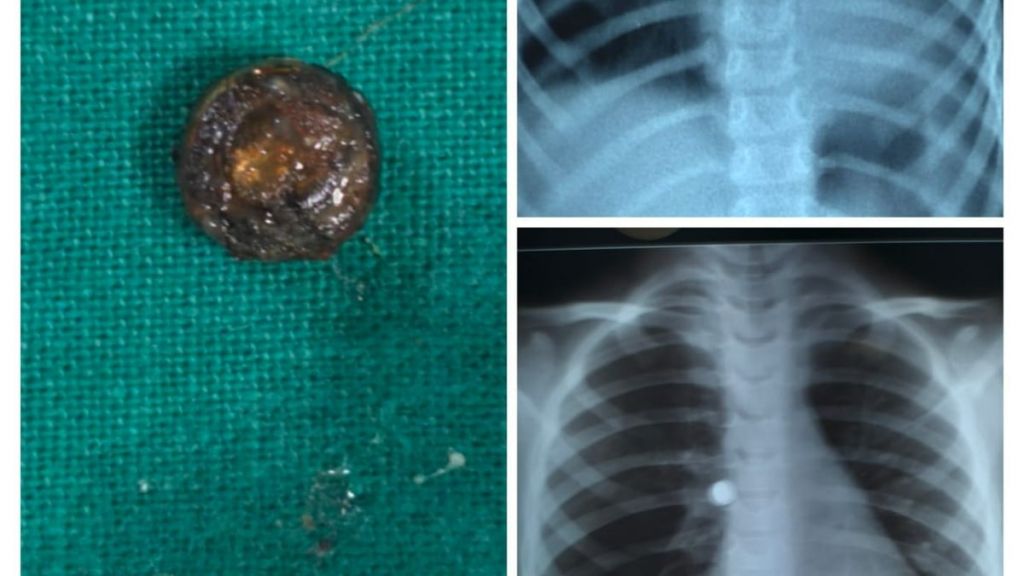
A 4-year-old girl was admitted to the emergency department of a hospital in Pune, after experiencing a sudden bout of coughing, which was later found to be caused by the accidental ingestion of a button battery while eating.
Initially, her parents took her to a pediatrician who treated her with medications and nebulization. Despite this, her wheezing persisted, prompting them to seek a second opinion. Further investigations revealed that a foreign object had lodged in her windpipe (bronchus). Realizing the potential for serious complications, the child was brought to another hospital for advanced care.
After thoroughly assessing her condition, Dr. Abhijit Benare performed an emergency bronchoscopy, after explaining the risks and potential complications to the concerned parents.
Here's how it was removed
Dr. Benare explained that the bronchoscopy successfully removed the button battery from the child’s bronchus. Fortunately, the patient’s recovery was smooth, and she was discharged on the third day following the procedure.
Dr. Tejas Hambir, Pediatrician & Intensivist, commented on the case, “Foreign body aspiration is common in children, with food items like peanuts and almonds being the typical culprits. However, the ingestion of a button battery is rare and poses unique risks.”
Dr. Benare further elaborated, “Button batteries can be extremely harmful as they release alkaline substances that can erode the bronchial cartilage. This can lead to life-threatening complications such as mediastinitis (inflammation in the chest cavity) and fistula formation, which may require major surgery if not treated promptly.”
Senior anaesthetist, Dr. Snehal Shool, highlighted the challenges in administering anaesthesia during such procedures, emphasizing that managing the procedure requires a high level of expertise due to the potential complications.
In this case, the prompt removal of the button battery was critical to the child’s recovery. Foreign body removal through bronchoscopy is the recommended treatment approach to prevent severe complications.